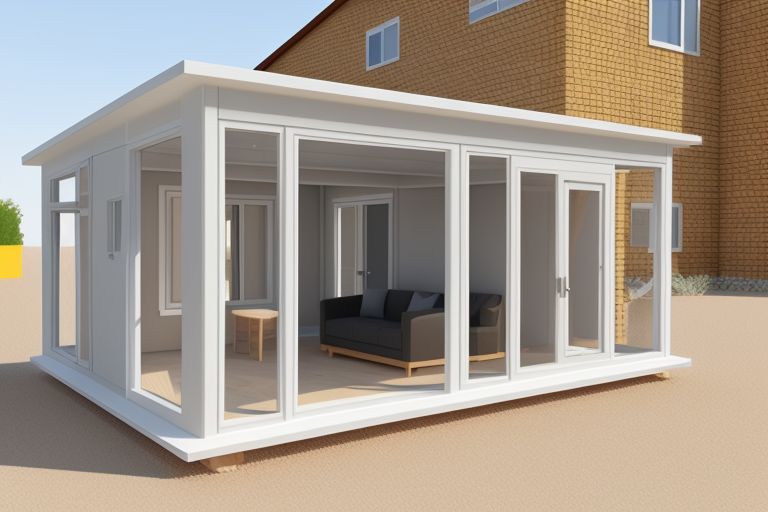
The construction industry is witnessing a technological revolution with the emergence of 3D printed homes, a method that promises to drastically reduce building times and costs while improving sustainability. This innovative approach to construction uses large-scale 3D printers to layer materials and build homes from the ground up in a fraction of the time it takes traditional construction methods.
The Emergence of 3D Printed Construction
3D printing technology, also known as additive manufacturing, has been around for decades, predominantly used in manufacturing for prototyping small-scale objects. However, recent advancements have enabled the scaling up of this technology to accommodate large-scale structures such as homes. These advancements include the development of more robust and versatile printing materials, more efficient printers, and refined printing processes.
How It Works
The process of 3D printing a home involves a computer-controlled printer that extrudes specially formulated cement-based mixtures, layer by layer, to construct walls and structural elements directly on-site. The printer follows a digital blueprint, which can be customized before or during construction, allowing for flexibility in design that traditional methods cannot match.
Benefits of 3D Printed Homes
Speed of Construction
One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing homes is the speed at which construction can be completed. A basic home can be printed in just 24 to 48 hours of print time—a dramatic reduction compared to several weeks or months required for conventional building methods.
Cost Efficiency
Reduced labor costs and decreased waste contribute to the cost efficiency of 3D printed homes. Since the printer can precisely deposit materials only where needed, there is minimal surplus and virtually no need for traditional raw materials like bricks and mortar, which further drives down costs.
Customization and Design Freedom
3D printing allows for complex architectural features to be created with the same ease as simple structures, opening up possibilities for personalized and innovative home designs that are both aesthetically appealing and functional.
Sustainability
This method of construction is more sustainable than traditional building techniques. The ability to use eco-friendly materials, such as recycled plastics or composites, and the significant reduction in waste make 3D printed homes a greener alternative.
Applications and Real-World Examples
3D printed homes are already a reality in several parts of the world. For example, in the Netherlands, a community of 3D printed homes has been created to address housing shortages and environmental concerns. Similarly, in rural areas and developing countries, this technology offers a rapid solution to housing crises caused by natural disasters or economic challenges.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its many benefits, the widespread adoption of 3D printed homes faces several challenges. Regulatory hurdles, including building codes and zoning laws, need to evolve to accommodate this new form of construction. Additionally, there is a need for further technological advancements to improve the quality and durability of printed structures.
The future of 3D printed homes looks promising, with continuous advancements in printer technology and material science. As these homes become more common and accepted, they have the potential to significantly alter the landscape of housing worldwide, making homes more affordable, accessible, and sustainable.
Conclusion
The revolution in construction brought about by 3D printing technology is just beginning. As we continue to innovate and improve upon this method, the dream of printing customized, cost-effective, and sustainable homes could become the standard practice in the near future. This transformative approach not only redefines what is possible in architecture but also holds the potential to solve some of the most pressing housing challenges faced globally.


















+ There are no comments
Add yours